Your Endocannabinoid System:
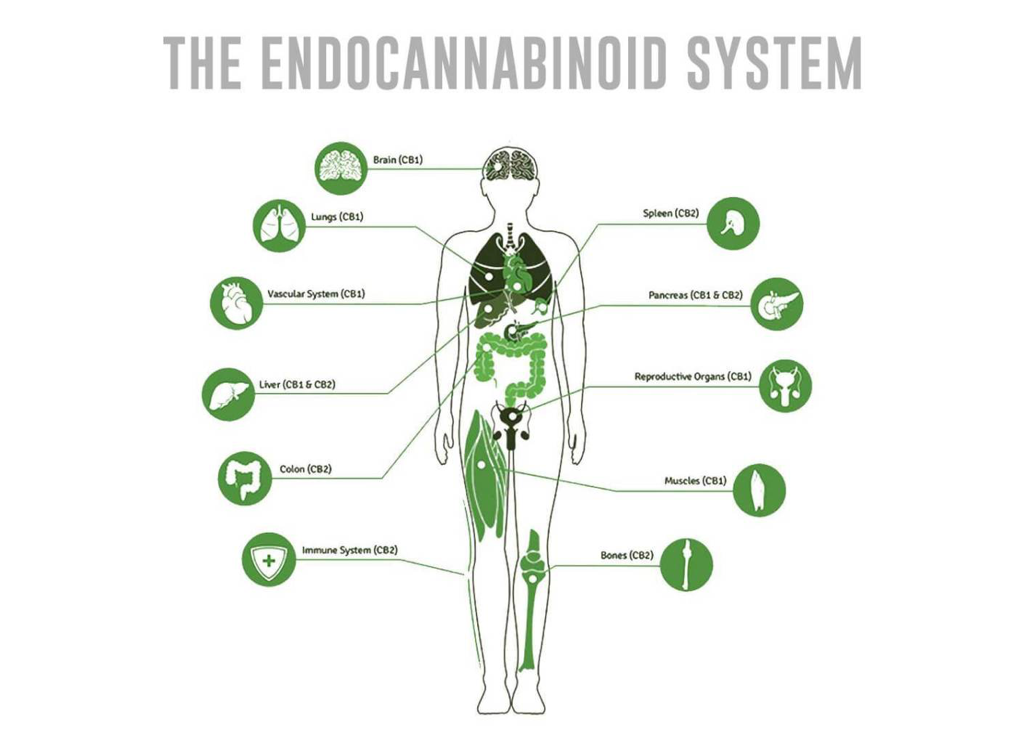
It may come as a surprise, but you were made for Cannabinoids. We all were. Every human (and most animals too) have an endocannabinoid system (ECS) with receptors throughout our bodies. This system is involved in almost all brain and body functions, from our ability to handle pain, stress and anxiety to our mobility and muscle health. In short, it keeps our bodies in balance.
The ECS can be described as an intricate physiological system utilizing cannabinoids produced in the body (endocannabinoids) and the receptors they attach to. The Endocannabioid system is a cell-signaling system, consisting of three main components: endogenous cannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. It is recently being referred to as the endocannabiome.
|
The role of the ECS in maintaining homeostasis, or a stable equilibrium, within the body can be summarized as “relax, eat, sleep, forget, and protect.” The ECS modulates everything from embryological development, to neural plasticity and neuroprotection. It also supports the immune system and promotes a healthy inflammatory response. The ECS is involved in cellular processes from apoptosis and carcinogenesis, the regulation of pain, hunger, satiety, feeding, and metabolism, to our emotional memory.
Disorders that have become associated with the ECS are numerous and, when taken together, represent the Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Syndrome (CEDS). The CEDS is caused by the bodies inability to produce or utilize endocannabinoids. CEDS describes a dysfunction in the ECS which contributes to a generalized breakdown in the body’s ability to maintain a stable equilibrium, known as homeostasis. This can lead to a variety of illnesses including migraines, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, and even depressive illnesses such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Other conditions which may in part be caused by CEDS include multiple sclerosis, Huntington’s, Parkinson’s, anorexia and even chronic motion sickness.
There are three ways to address CEDS. First, you can increase the amount of endocannabinoids produced by the body. Second, you can decrease the rate at which endocannabinoids are degraded. Third, you can increase the number of receptors and improve their function.
Disorders that have become associated with the ECS are numerous and, when taken together, represent the Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Syndrome (CEDS). The CEDS is caused by the bodies inability to produce or utilize endocannabinoids. CEDS describes a dysfunction in the ECS which contributes to a generalized breakdown in the body’s ability to maintain a stable equilibrium, known as homeostasis. This can lead to a variety of illnesses including migraines, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, and even depressive illnesses such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Other conditions which may in part be caused by CEDS include multiple sclerosis, Huntington’s, Parkinson’s, anorexia and even chronic motion sickness.
There are three ways to address CEDS. First, you can increase the amount of endocannabinoids produced by the body. Second, you can decrease the rate at which endocannabinoids are degraded. Third, you can increase the number of receptors and improve their function.
Cannabinoid Receptors:
|
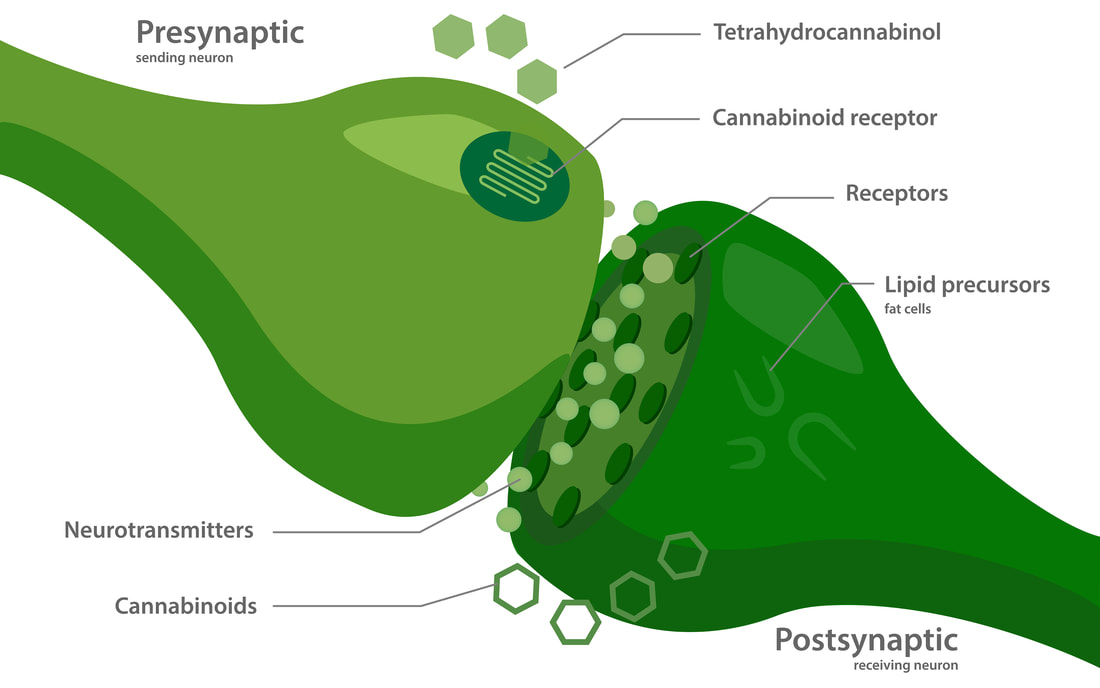
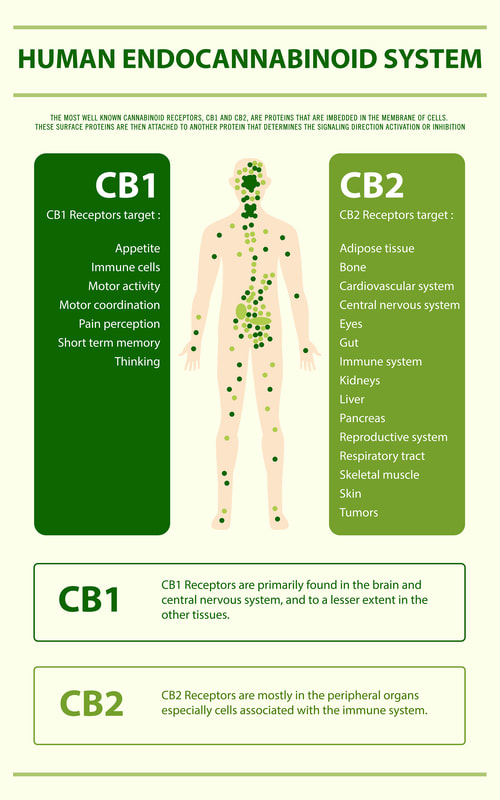
There are three cannabinoid receptors associated with our ECS – CB1, CB2, and TRPV1. These receptors play an important role in vital bodily homeostasis, health, and healing. The receptors are not found everywhere in our body though, they persist in areas involved in important processes like coordination & movement, appetite, emotions, memory, and pain. CB1 is largely found in the brain and holds a key role in our neurological processes. CB2 can be abundant in immune cells, the digestive system, and the peripheral nervous system. TRPV1 is involved in pain response, inflammation, and regulation of body temperature. It is actually the attachment site for capsaicin – the compound known for the burning sensation we experience when eating hot peppers.These receptors are important, but they do nothing without the substances that attach to them and allow them to activate – the endogenous cannabinoids that our bodies produce (yes your body actually produces cannabinoids!) AEA (anandamide) and 2-AG are the most studied cannabinoids. Both of these can attach to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Think of them as the keys that open up the same locks. Depending on which key is used, different doors will open. When our ECS becomes imbalanced, the important functions that it regulates can go haywire. This happens when receptors are over or under active, and endocannabinoid levels are too low or too high. An imbalanced ECS can be treated with conventional medication, supplements, lifestyle choices and alternative therapies that all activate the cannabinoid receptors within our bodies. Probiotics modulate CB1 activity, acupuncture increases CB2 in skin tissues, intense exercise increases AEA which is why we experience the “runner’s high.”
|
What is PEA?
- An Endogenous or Endo-“Cannabinoid” (Comes from Inside Your body)
- Natural fatty acid amide produced by our own bodies (“Endocannabinoid Family”’)
- Produced locally in all our tissues in response to stress, pain and inflammation
- Works indirectly on Receptors in your body’s Endocannabinoid System
- Promotes Balance and Homeostasis of your ECS
- Works on a receptor in your body related to chronic pain and inflammation.
- Has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, neuroprotective, and anticonvulsant properties.
- Natural and Safe
- Enhances synergistic Entourage effect of CBD and other Endo- and Phyto- Cannabinoids.
PEA utilizes the endocannabinoid system, affecting several different nuclear receptors, either by binding to them directly, or through “entourage effect”. PEA plays a major role in reducing chronic pain and excessive inflammation, but also in regulating immune response and feeding. A great advantage of PEA is that it does not mask the pain, but it actually works to remove its source.
Unlike CBD, PEA is structurally related to anandamide and may co-enhance its effects as well as inhibit FAAH, which degrades anandamide. PEA also helps stimulate the production of endocannabinoids in the body’s endocannabinoid system. Although biogenetically and chemically different, CBD and PEA share a remarkable series of pharmacological similarities. For example, PEA counteracts endotoxin-induced inflammation in cells in the same cell lineage as CBD. CBD and PEA also share a number of centrally mediated effects which include neuroprotection and reduction of seizure activity.
Unlike CBD, PEA is structurally related to anandamide and may co-enhance its effects as well as inhibit FAAH, which degrades anandamide. PEA also helps stimulate the production of endocannabinoids in the body’s endocannabinoid system. Although biogenetically and chemically different, CBD and PEA share a remarkable series of pharmacological similarities. For example, PEA counteracts endotoxin-induced inflammation in cells in the same cell lineage as CBD. CBD and PEA also share a number of centrally mediated effects which include neuroprotection and reduction of seizure activity.
What is CBD? THC?
Phytocannabinoids are the substances found in plants (mainly cannabis sativa) and they are able to stimulate the ECS receptors. The most well known and studied phytocannabinoid for ECS stimulation is THC, however this molecule’s non-psychoactive counterpart, CBD, is also able to modulate the structure of the ECS without getting “high.” While THC attaches itself directly to the CB1 and CB2 receptors (like AEA and A2-G), CBD attaches to a different receptor site of CB1. By attaching to a different area it is able to change the shape of the receptor which has an influence on how the receptor will interact with other substances that bind to it. CBD can influence the ECS in other ways too, by supressing the enzyme that breaks down AEA. By blocking this enzyme, AEA has the chance to have a longer effect on the receptor, thus prolonging the positive effects that we seek in using CBD oil as a pain supplement or other form of treatment.
CBD can also directly attach to TRPV1 and other receptors that play a role in our neurological and cardiovascular systems. This is why CBD works so well as a treatment for neurological issues like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease. If you didn’t already know, big pharma has released a drug called Epidolex that is now FDA approved and prescribed by doctors specifically for treating symptoms associated with epilepsy. CBD companies offering premium products that are all natural, lab tested, and organically grown are becoming the way of CBD use for many users who are seeking a healthier alternative to conventional medicine.
CBD can also directly attach to TRPV1 and other receptors that play a role in our neurological and cardiovascular systems. This is why CBD works so well as a treatment for neurological issues like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease. If you didn’t already know, big pharma has released a drug called Epidolex that is now FDA approved and prescribed by doctors specifically for treating symptoms associated with epilepsy. CBD companies offering premium products that are all natural, lab tested, and organically grown are becoming the way of CBD use for many users who are seeking a healthier alternative to conventional medicine.
Though CBD is generally well tolerated and considered safe, it may cause adverse reactions in some people.
Side effects noted in studies include:
- Diarrhea
- Changes in appetite
- Fatigue
- Potential Liver Disease
Click here to See More information on potential side effects.
Double-tap to edit.