What is Psoriasis?
|
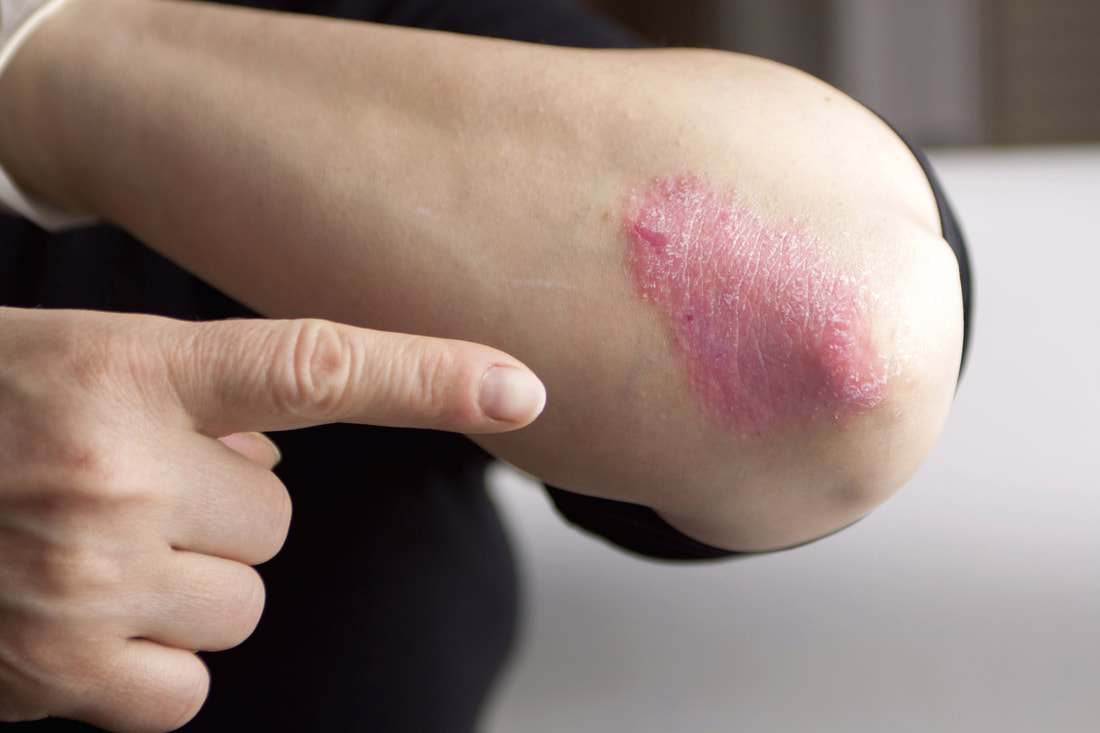
Psoriasis is a genetic disease which causes chronic inflammation and scaling on skin. Psoriasis is charecterised by skin cells that multiply up to 10 times faster than normal below the surface of the skin and get deposited on the surface before they get matured. Normally, this deposition of cells takes a month time however, in psoriasis it may occur within few days. When these cells reach surface and die, raised, red plaques covered with white scales form. Psoriasis begins as a small scaling papule. When multiple papules coalesce, they form scaling plaques.
Development of thick patches of inflamed skin with a silvery scale covering starts to appear on skin. These patches are also referred to as plaques as they itch and feel sore. The commonly affected areas are knees, elbows, other parts of the legs, lower back, scalp, soles of feet, face and palms. Psoriasis can also affect toenails, fingernails, inside the mouth and soft tissues of genitals. |
Inflammation with Psoriasis results when the T-cells accidently get involved and become active triggering other immune responses, resulting in inflammation and rapid turnover of skin cells. A major source of developing the disease is its presence in the family history of an individual. There are several forms of psoriasis, including guttate psoriasis, plaque psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. Conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular problems, obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes are more likely to develop in a person with psoriasis. The most common types of psoriasis are plaque psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, and pustular psoriasis.
Psoriasis Cures? Treatments?
The treatment options of psoriasis include topical treatment, phototherapy, and systemic treatment. Topical treatment includes application of ointment or cream forms of corticosteroids, vitamin D3, retinoids, coal tar, or anthralin. Other medical options include phototherapy (ultraviolet B and photochemotherapy), and systemic medication (methotrexate, acitretin, cyclosporine, etanercept, and infliximab). Moreover, lifestyle modifications, such as diet and alternative therapies are also common components of psoriasis treatment regimens.
Topical is the Best Treatment Option
The majority of the research being done and treatments are being developed for topical administration. It has been found that the topical route of administration is easy to use, non-invasive, and ensures high level of patient satisfaction, and thus, improves patient’s compliance toward medications for the treatment of the disease.
RESEARCH ARTICLES, WITH SELECT QUOTES
click on buttons for quote source and Full Research documents and articles.
Vitamin D possesses different health benefits that can help treat several types of psoriasis, including scalp psoriasis.
A studyTrusted Source from 2011 found that vitamin D can strengthen the immune system. Because psoriasis is an autoimmune response, this effect could help treat the condition internally.
Topical oils and ointments for psoriasis containing vitamin D can also help treat flares. Vitamin D can slow the growth of new cells, so vitamin D oil applied directly to the flare can help thin the plaque.
"Many relatable skin disorders and abnormalities such as psoriasis, vitiligo, eczema and urticaria can be linked to vitamin D deficiency and at the very least, vitamin D could help these conditions."
"According to Dr. Dennis Gross, one of the few dermatologists to hone in on vitamin D research, it also helps minimize acne, boost elasticity, stimulate collagen production, enhance radiance, and lessen lines and the appearance of dark spots."